Having employees work outside the office adds another layer of complexity to management. HVAC, health care, construction and other similar industries commonly need to consider how best to approach field services management (FSM). Efficiently managing field employees can improve customer satisfaction, increase employee engagement and cut costs. Here are some insights on current and future FSM trends.
In this article:
- Field service management processes
- Tips and best practices for effective FSM
- Downloadable chart to compare FSM software
- Examples of how different industries use FSM
- Trends to watch
What Is Field Service Management?

Field Service The board (FSM) alludes to the most common way of planning and enhancing the tasks of a business’ field-based labor force and assets. It incorporates the administration of undertakings, for example, planning, dispatching specialists, following position progress, keeping up with stock, and guaranteeing excellent assistance conveyance. FSM is normally utilized in ventures where representatives perform administrations on location, like utilities, media communications, development, and medical services.
Key Features of Field Service Management

- Work Planning and Dispatching:
- Doling out assignments to the right expert in light of abilities, area, and accessibility.
3 Stock and Resource The executives:
• Monitoring instruments, parts, and gear to guarantee field groups have what they need.
Diminishing postpones brought about by absent or lost stock.
4 Continuous Following:
- Keeping track of tools, parts, and equipment to ensure field teams have what they need.
- Reducing delays caused by missing or misplaced inventory.
- Real-Time Tracking:
- Monitoring the location and progress of technicians in real time.
- Enhancing visibility for managers and improving response times.
- Customer Communication:
- Automating updates and notifications about appointment times and service progress.
- Ensuring transparent communication to improve customer satisfaction.
- Investigation and Announcing
- Gathering and investigating information on key execution pointers (KPIs, for example, first-time fix rates, work fruition times, and consumer loyalty.
Utilizing experiences to enhance activities and decrease failures.Advantages of FSM
• Expanded Proficiency: Computerization of routine errands like planning and dispatching lessens managerial weights.
Benefits of FSM

- Increased Efficiency: Automation of routine tasks like scheduling and dispatching reduces administrative burdens.
- Further developed Consumer loyalty: Ideal and exact assistance conveyance improves client experience.
- Cost Investment funds: Enhanced planning and asset allotment lessen fuel, work, and functional expenses.
- Better Asset Usage: Guarantees professionals are furnished with the essential devices and data to proficiently finish jobs.
FSM in Practice
Field Service The board is frequently worked with by specific FSM programming, which incorporates different capabilities into a concentrated stage. These apparatuses give highlights like GPS following, cloud-based information capacity, and high level planning controlled by man-made reasoning Examples of popular FSM software include Sales force Field Service, Service Titan, and Oracle Field Service.
Industries That Use FSM
- Utilities: Maintenance of power lines, water systems, and gas networks.
- Telecommunications: Installing and repairing internet and cable services.
- HVAC and Home Services: Servicing residential and commercial properties.
- Healthcare: Managing equipment repair and mobile medical services.
- Construction and Maintenance: Overseeing site operations and equipment
Benefits of Field Service Management
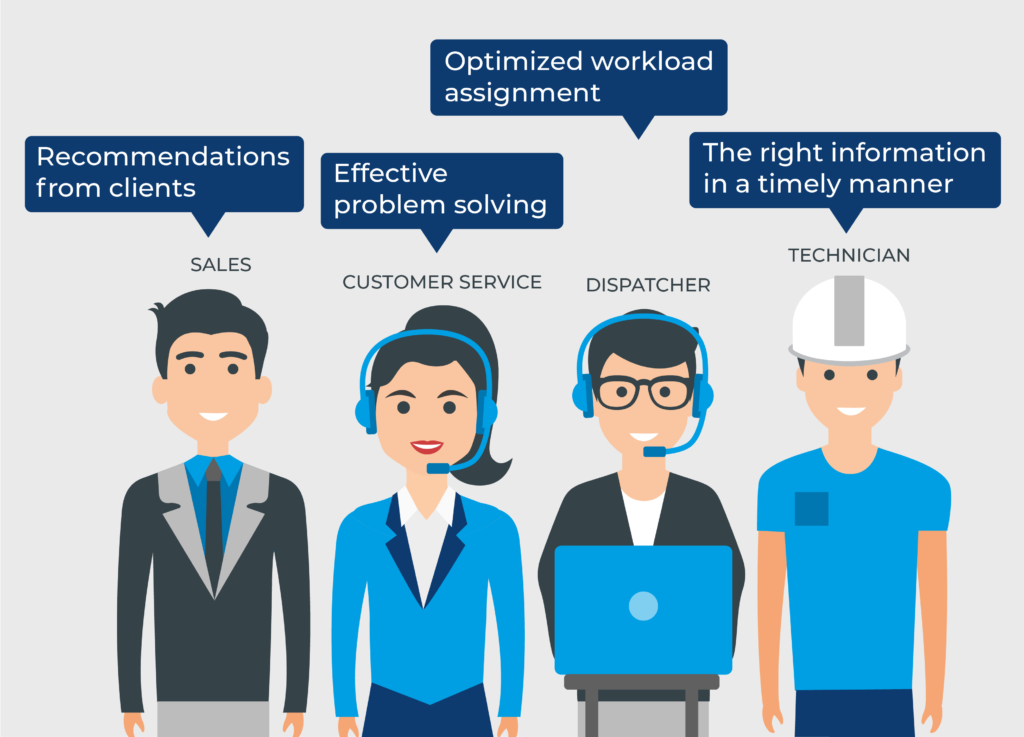
Field Service The board (FSM) offers various advantages that upgrade functional productivity, lessen costs, and further develop consumer loyalty.Below are the key advantages of implementing FSM systems and processes:
1 . Worked on Functional Effectiveness
Improved Booking: High level FSM devices use calculations to allot undertakings in light of variables like expert accessibility, nearness, and range of abilities, decreasing postponements and covers.
• Decreased Free time: Constant updates and effective dispatching guarantee that field experts invest less energy pausing and additional time on useful errands.
• Smoothed out
Work processes: Mechanization of authoritative undertakings, for example, work logging and invoicing, saves time for administrators and field laborers.
2. Enhanced Customer Experience
- Faster Response Times: Efficient scheduling and dispatching help field teams reach customers sooner, especially in emergencies.
• Straightforward Correspondence: Clients get refreshes on arrangement times, administration progress, and assessed finishing times, building trust.
• Higher Fulfillment Rates: Convenient and quality help conveyance, joined with constant input instruments, further develops generally consumer loyalty
3. Cost Savings
• Diminished Travel Expenses: Upgraded courses limit fuel utilization and travel costs.
• Proficient Asset Assignment: By better matching experts to occupations, organizations keep away from overstaffing or underutilization.
• Limited Hardware Misfortune: Constant stock administration lessens misfortunes and guarantees apparatuses are promptly accessible when required..
4. Increased Productivity
Mobile Enablement: Technicians equipped with mobile apps can access job details, upload photos, and complete documentation on the go.
• First-Time Fix Rates: FSM devices furnish professionals with definite client history and indicative apparatuses, empowering them to determine issues on the primary visit.
• Execution Observing: Administrators can follow key measurements like work culmination times and professional use to distinguish and address bottlenecks.
5. Better Resource Management
• Stock and Resource Control: FSM frameworks track parts and gear, guaranteeing experts have the important devices and lessening postpones brought about by missing things.
• Proactive Upkeep: Prescient investigation assist organizations with keeping up with hardware before breakdowns happen, staying away from exorbitant fixes..
6. Information Driven Navigation
Complete Revealing: FSM stages give experiences into measurements like work span, consumer loyalty, and expert effectiveness. Trend Analysis: Historical data helps forecast demand and allocate resources effectively.
Ceaseless Improvement: Information permits organizations to refine processes and further develop execution after some time.
7. Compliance and Safety
- Regulatory Adherence: FSM systems ensure services are delivered according to industry standards and regulations.
- Safety Protocols: Digital checklists and real-time communication enhance worker safety and compliance during field operations.
8. Scalability
- Adapting to Growth: FSM tools can scale with a growing workforce or expanding service areas, ensuring seamless operations as the business evolves.
- Integration with Other Systems: Modern FSM solutions integrate with CRM, ERP, and IoT systems for a unified operational approach.
Difficulties of Field Administration The executives
Field Administration The executives (FSM) accompanies its own arrangement of difficulties that organizations should address to guarantee smooth and proficient tasks. These difficulties originate from the intricacies of overseeing field groups, planning assets, and meeting client assumptions. The following are the critical difficulties of FSM
1. Labor force Planning and Dispatching
• Ability Coordinating: Doling out the right professional with the proper abilities to the right errand can be complicated, particularly for specific positions.
• Last-Minute Changes: Unanticipated issues like abrogations, deferrals, or crises disturb plans, requiring quick changes.
• Geological Limitations: Overseeing scattered groups across wide regions adds calculated difficulties, especially in provincial or difficult to-arrive at areas.
2. Communication Gaps
• Absence of Ongoing Updates: Without constant specialized devices, dispatchers and professionals might confront defers in sharing basic data.
• Client Association: Unfortunate correspondence with clients about postponements or administration updates can prompt disappointment and negative audits.
3. Inventory and Resource Management
- Stock Shortages: Tracking and maintaining adequate inventory levels for tools and spare parts can be challenging, leading to delays in task completion.
- Resource Misplacement: Mismanagement of tools or equipment can result in inefficiencies and increased operational costs.
4. Integration with Technology
• Intricacy of FSM Programming: Taking on new FSM arrangements can be overpowering for workers who are new to innovation.
• Framework Reconciliation: Incorporating FSM programming with existing frameworks like CRM, ERP, or IoT stages can be convoluted and tedious.
• Information Security Dangers: With the ascent of cloud-based FSM frameworks, it is basic however testing to guarantee information security and consistence.
5. High Operational Costs
• Travel Costs: Rising fuel costs and wasteful directing increment costs for field tasks.
• Extra time Expenses: Unfortunate booking or startling help requests can prompt extreme extra time installments.
6. Performance Monitoring
- Limited Visibility: Without effective tracking tools, managers may struggle to monitor technician performance, progress, and location in real time.
- Accountability: Ensuring technicians follow schedules, safety protocols, and customer service standards can be difficult.
7. Give Complete Preparation
• Specialized Abilities Improvement: Constantly train professionals to stay aware of new innovations and industry principles.
• Delicate Abilities Preparing: Train professional’s client care best practices to further develop communications and fulfillment.
Administrative and Consistence Issues
• Evolving Guidelines: Staying aware of industry-explicit consistence norms and guidelines requires constant updates and preparing.
• Security Concerns: Guaranteeing laborer wellbeing in risky circumstances and consistence with wellbeing conventions can challenge.
9. Overseeing Occasional Interest
• Fluctuating Jobs: Certain ventures face occasional pinnacles that make labor force and asset designation troublesome.
• Transitory Labor force: Recruiting and preparing impermanent staff for top seasons can prompt irregularities in help quality.
.
10. Data Overload
• Disorderly Information: The sheer volume of information from different sources (client input, IoT gadgets, professional reports) can overpower organizations.
• Significant Bits of knowledge: Removing significant experiences from gathered information requires progressed examination apparatuses, which may not be accessible all of the time.
Addressing These Challenges
To overcome these hurdles, businesses can:
• Embrace Current FSM Arrangements: Use cloud-based FSM instruments with simulated intelligence and continuous following abilities.
• Give Progressing Preparing: Furnish specialists and staff with the abilities to utilize new advances and follow best practices.
• Upgrade Correspondence Frameworks: Carry out apparatuses that empower consistent correspondence between field groups, dispatchers, and clients.
• Influence Prescient Investigation: Use information bits of knowledge to conjecture interest, upgrade stock, and further develop independent direction.
Step by step instructions to Further develop Field Administration Tasks
How to Further develop Field Administration Tasks?
Further developing field administration tasks includes streamlining work processes, utilizing innovation, and cultivating a client centered culture.
1. Optimize Scheduling and Dispatching
- Use Automated Tools: Leverage FSM software to schedule jobs efficiently, match tasks with the right technicians, and minimize travel time.
- Dynamic Booking: Execute frameworks that permit ongoing acclimations to plans for latest possible moment changes or crises.
- Ability Based Tasks: Guarantee professionals are matched to undertakings in light of their mastery to increment first-time fix rates.
2. Invest in FSM Technology
• Versatile Arrangements: Outfit specialists with portable applications that give admittance to work subtleties, route, and specialized instruments.
• Constant Following: Use GPS and IoT gadgets to screen expert areas, work progress, and gear status.
• Cloud-Based Stages: Concentrate information capacity to further develop availability and coordinated effort across groups.
3. Enhance Communication
• Smooth out Interior Correspondence: Utilize texting or coordinated specialized instruments to interface field laborers with supervisors and care staff.
• Keep Clients Informed: Give continuous updates about arrangement windows, deferrals, and administration progress to oversee assumptions.
4.Focus on Inventory and Resource Management
• Track Stock Progressively: Use stock administration frameworks to guarantee specialists have the essential devices and parts for their positions.
• Take on Prescient Upkeep: Screen gear execution and timetable preventive support to lessen breakdowns and administration interruptions.
5. Provide Comprehensive Training
- Technical Skills Development: Continuously train technicians to keep up with new technologies and industry standards.
- Soft Skills Training: Teach technicians customer service best practices to improve interactions and satisfaction.
- Technology Training: Ensure all employees can effectively use FSM software and mobile tools.
6.Collect and Leverage Data
• Screen Key Measurements: Track KPIs like first-time fix rates, work fulfillment times, and consumer loyalty scores.
• Investigate Patterns: Utilize verifiable information to recognize designs, expect request, and upgrade activities.
• Execute Criticism Circles: Assemble input from specialists and clients to distinguish regions for development.
7. Improve First-Time Fix Rates
- Provide Comprehensive Job Details: Ensure technicians have all necessary information, such as service history and troubleshooting guides.
- Pre-Visit Diagnostics: Use IoT and remote diagnostics to identify and resolve potential issues before technicians are dispatched.
8. Foster a Customer-Centric Approach
- Personalize Service: Use CRM data to understand customer preferences and provide tailored experiences.
- Proactive Communication: Notify customers of updates and delays promptly to build trust.
- Follow-Up After Service: Collect feedback post-service to measure satisfaction and address any concerns.
9. Adopt Scalable Systems
• Pick Adaptable FSM Programming: Decide on arrangements that can develop with your business, obliging more specialists or administration regions depending on the situation.
• Incorporate with Different Frameworks: Connection FSM stages with CRM, ERP, and bookkeeping frameworks for a consistent functional stream.
10. Embrace Sustainability
- Optimize Routes: Reduce fuel consumption and environmental impact with efficient routing algorithms.
- Use Eco-Friendly Tools: Invest in energy-efficient tools and vehicles to align with sustainability goals.
11. Regularly Review and Refine Processes
- Conduct Performance Audits: Periodically evaluate field service processes to identify bottlenecks.
- Engage Employees in Planning: Involve technicians in decision-making to gain practical insights and foster a sense of ownership.
12. Offer Incentives for Excellence
• Reward Superior workers: Perceive and boost specialists who meet or surpass execution objectives.
• Empower Coordinated effort: Advance cooperation through bunch motivations and shared execution objectives.
While picking Field Administration The board (FSM) programming, having an agenda guarantees you select an answer that lines up with your business needs. Here’s a comprehensive FSM software checklist to guide your decision:
User Experience
- Ease of Use
- Intuitive user interface for managers, technicians, and customers.
- Minimal learning curve with robust user guides and tutorials.
- Customization
- Ability to tailor workflows, forms, and reports to business needs.
- Configurable user roles and permissions.
- Multilingual Support
- Support for multiple languages to accommodate diverse teams.
Support and Scalability
- Vendor Support
- • every minute of every day client service through different channels (telephone, visit, email).
- Access to training resources and implementation support.
- Scalability
- Capability to handle more users, jobs, or service areas as the business grows.
- Flexibility to add new features or modules as needed.
- Updates and Maintenance
- Regular software updates with new features and security patches.
- Minimal downtime during updates or maintenance.
Cost and ROI
- Pricing Model
• Straightforward evaluating with no secret charges.
• Adaptable plans (e.g., membership based, pay-per-use).
2. Profit from Speculation
- Demonstrated potential to reduce operational costs and improve efficiency.
- Tools to measure ROI from software adoption.
Additional Features
- AI and Automation
- Predictive analytics for preventive maintenance and demand forecasting.
- Chatbots for customer communication and query handling.
- Collaboration Tools
- Shared platforms for technicians and back-office staff.
- Real-time updates to enhance teamwork.
- Sustainability Features
- Tools for carbon footprint tracking and sustainability reporting.
- Energy-efficient route planning.