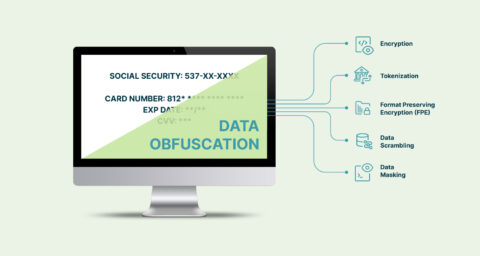
What’s the significance here to be GDPR compliant?
At its center, GDPR compliance implies an association that falls inside the extent of the Overall General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) meets the necessities for appropriately dealing with individual information as characterized in the law.
The GDPR compliance frames specific commitments associations should follow, which limit how individual information can be utilized.
It also defines eight data subject rights that guarantee specific entitlements for an individual’s personal data. Ultimately giving individuals more autonomy over their personal information and how it is used.

Outline of the GDPR
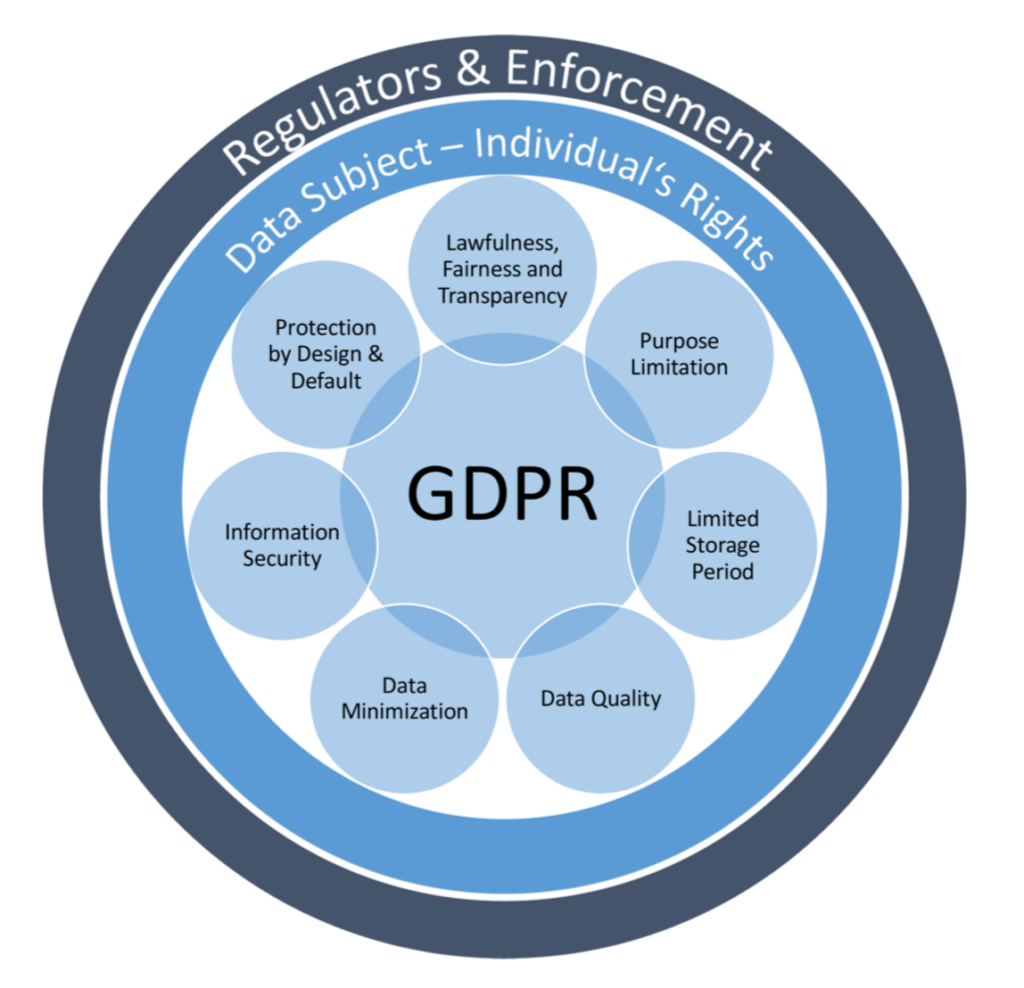
GDPR compliance is the most grounded worldwide protection regulation essentially today. Made by the European Union (EU) to control how associations gather, handle, and safeguard individual information of EU inhabitants. The GDPR produced results on May 25, 2018, and is a limiting guideline composed straightforwardly into Part States’ regulations. It is intended to fortify security freedoms by giving information subjects control of how their own information is gotten, utilized, and shared.
The GDPR compliance was put forth considering three primary objectives:
Lay out and safeguard the key protection privileges of people.
Bring together security regulations across the EU by supplanting the 28 individual EU part-state regulations and the past 1995 Information Insurance Mandate.
Adapt privacy laws that reflect the change the technology landscape has made on personal data over the last 25 years.
GDPR compliance terminology
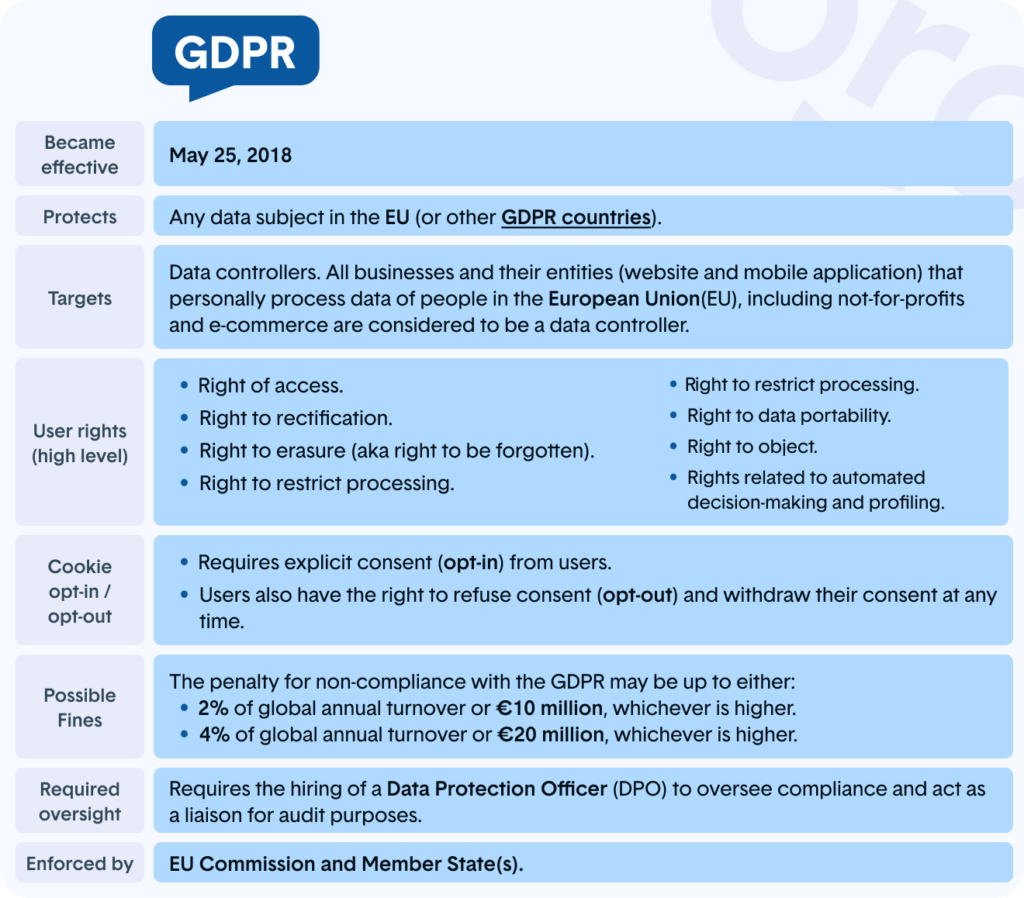
How about we characterize a portion of the essential wording of the GDPR before we dive into the subtleties?
- An information subject is any individual officially living in the EU who has their information gathered, held, or handled by a regulator or processor.
- Information regulator alludes to the substance answerable for deciding the reason and legal reason for handling individual information.
- The information processor, who teams up with the information regulator, alludes to the individual liable for handling individual information in the interest of the regulator.
- Handling includes any computerized or manual activity or set of tasks performed on private information or sets of individual information, including the assortment, recording, association, organizing, capacity, variation or modification, recovery, etc.
- Individual information alludes to any data connected with a characteristic individual (‘information subject’) that can straightforwardly or by implication distinguish that individual as it connects with their private, expert, or public life, including a name, email address, photographs, or even bank proclamations.
- Getting the assent of the information subject alludes to any “uninhibitedly given, explicit, informed, and unambiguous sign” that the information subject consents to the handling of individual information connected with them. Information subjects can give assent to either an explanation or unequivocal governmental policy regarding minorities in society.
Does the GDPR compliance apply to your association?

To conclude whether you are covered under the GDPR, you want to think about both the material extension’ (i.e., whether your handling movement is managed by the GDPR) and the regional degree’ (i.e., whether you are in a ward where the GDPR applies).
Does the GDPR compliance concern US organizations?
US associations might fall inside the scope of the GDPR. To decide if your association should go along, a similar examination should be applied by taking a gander at the material and regional extent of the law illustrated underneath. To put it plainly, assuming your association processes (i.e., gathers, records, structures, stores, adjusts, utilizes, uncovers, deletes, and so on) individual data of somebody living in the EU for the trading of labor and products or for the motivations behind observing the way of behaving of EU-residents, then you probably fall inside the extent of the GDPR.
The material scope
GDPR compliance applies to the handling of individual information done entirely or incompletely via mechanized implies. It likewise applies to the handling that doesn’t utilize computerized implies yet frames part of a recording framework or is planned to shape part of a documenting framework. This covers most exercises that associations do with information, including gathering, recording, putting away, getting to or seeing, utilizing, dissecting, consolidating, uncovering, or erasing individual information.
The regional degree: Does the GDPR apply outside the EU?
GDPR compliance applies to the handling of individual information by a regulator or a processor laid out in the EU, whether or not the handling happens in the EU.
It likewise has an extraterritorial application for a regulator or processor that isn’t laid out in the EU in the event that the regulator or the processor offers labor and products to information subjects in the EU or screens information subjects’ conduct occurring in the EU. For instance, the GDPR applies to a US web-based shopping site that draws in and offers products to clients in the EU.
The offering of goods and services could be complimentary, free of charge. This could cover foreign government agencies or non-profit organizations. For example, the GDPR applies to a travel information page run by a US state government that collects personal information such as IP addresses while the site visitors from the EU access the free travel information.
What are GDPR compliance information subject freedoms?
- The GDPR frames eight crucial information subject freedoms, in addition to one side to pull out assent. We should investigate these privileges:
- Right to be educated
- Information subjects reserve the option to be educated about the assortment and use regarding their own information.
- Right to get to
- Information subjects reserve the option to view and demand duplicates of their own information.
- Right to amendment
- Information subjects reserve the privilege to demand off-base or obsolete individual data be refreshed or amended.
- Right to be neglected/Right to eradication
- Information subjects reserve the option to demand their own information be erased. Note that this is definitely not an outright right and might be dependent upon exceptions in light of specific regulations.
- Ideal for information compactness
- Information subjects reserve the option to request their information to be moved to one more regulator or given to them. The information should be given in a machine-discernible electronic organization.
- Right to limit Handling
- Information subjects reserve the option to demand the limitation or concealment of their own information.
- Right to pull out assent
- Information subjects reserve the option to pull out recently given agree to deal with their own information.
- Right to protest
- Information subjects reserve the privilege to protest the handling of their own information.
- Right to protest robotized handling
- Information subjects reserve the option to protest choices being made with their information exclusively founded on mechanized direction or profiling.
11-step GDPR compliance checklist
Now that we comprehend the fundamentals, how about we hop into the means your association can take to meet GDPR consistency? GDPR consistency can look a bit changed relying upon your association, yet there are explicit advances any association can take now to make a GDPR consistent security program